Research
My research activity broadly focuses toward a deeper understanding the structure-function relationship of bio(molecules), and mechanism of action, thermodynamic and kinetic insights of physicochemical processes in gas-phase as well as in condensed-phase spanning multiple time and length scales, calculating atomistic details applying the force field approach to the high-level electronic details using the quantum chemical methods.
Chemical Reaction Dynamics
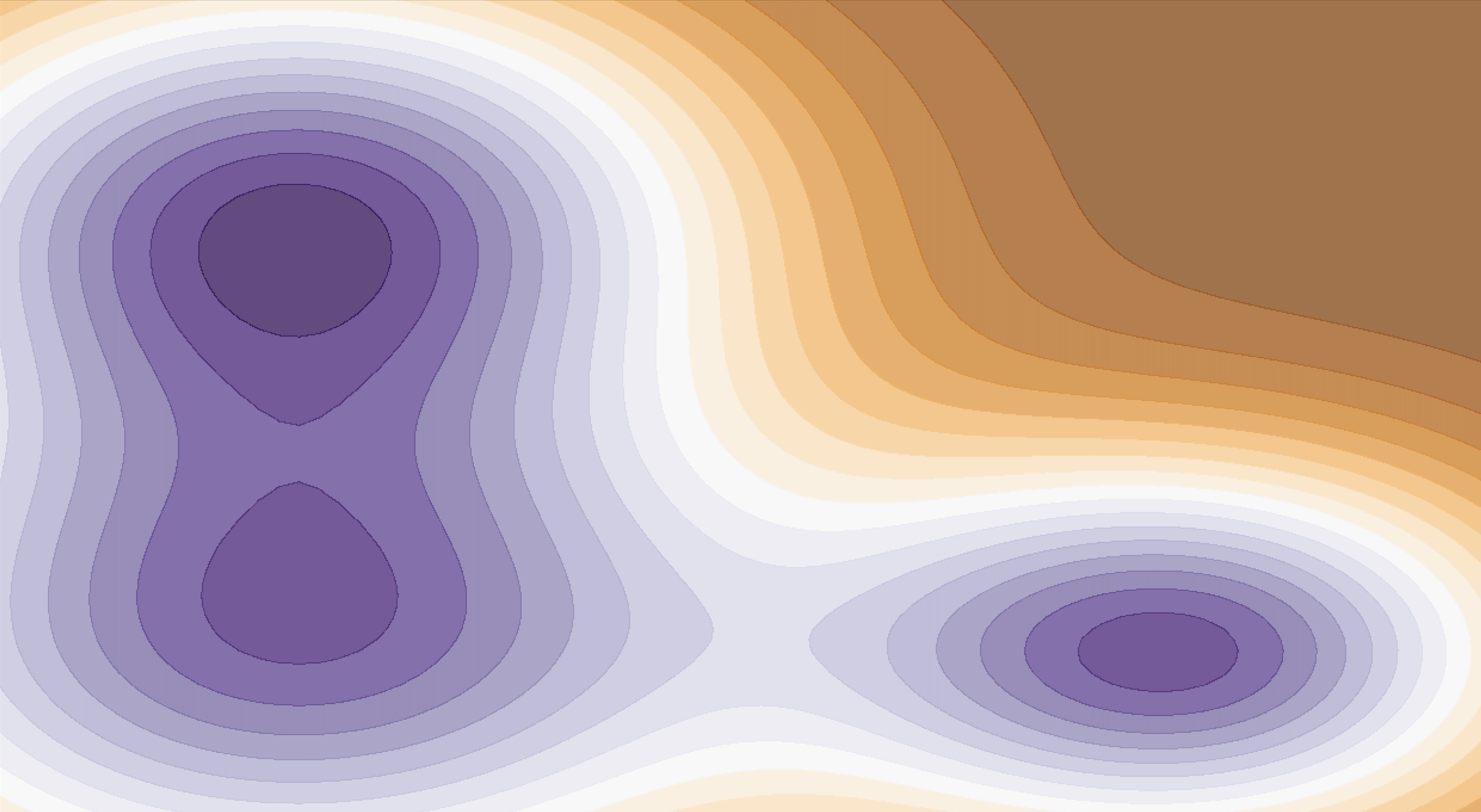
Machine Learning Force Fields (MLFF)
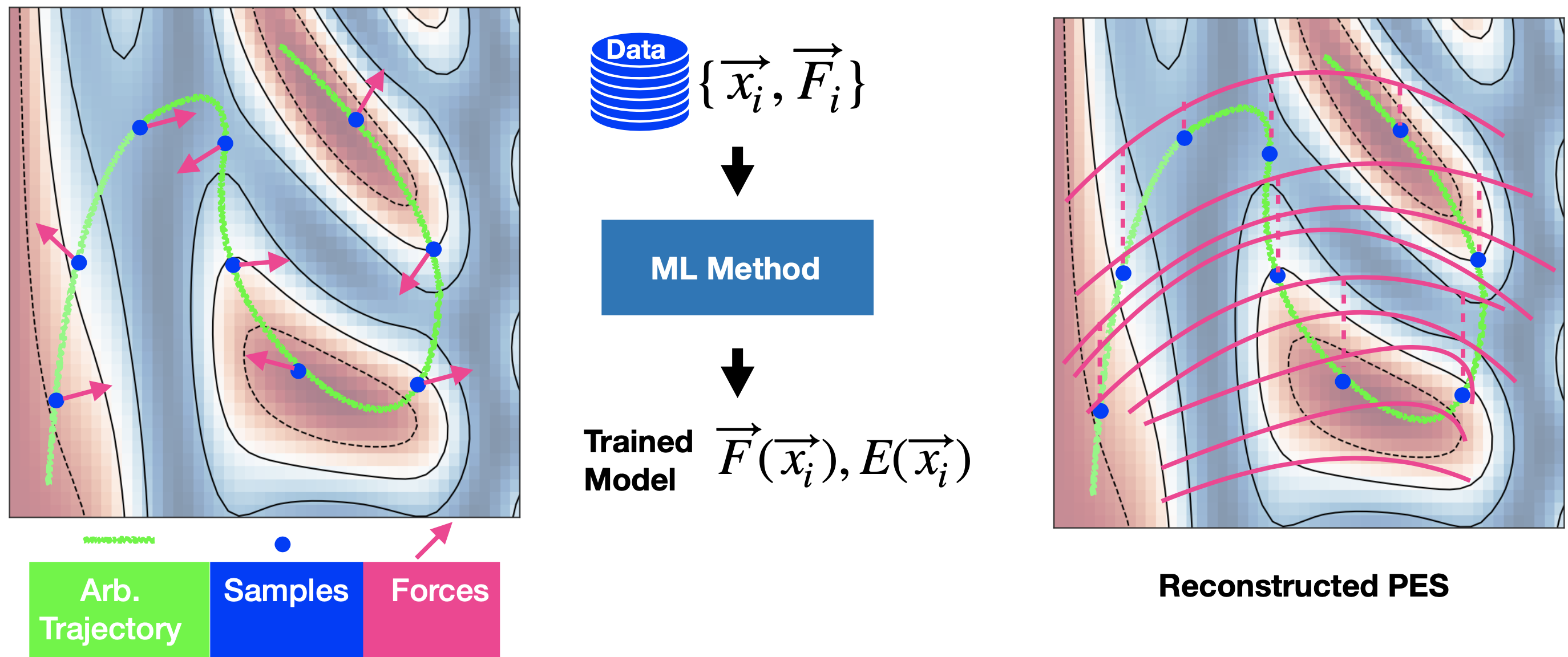
An ML model is trained using an arbitrary set of data points which are the inputs for the ML method that outputs the reconstructed force fields and the potential energy surface (PES).
AIMD Detection of Planar Tetracoordinated Transition State
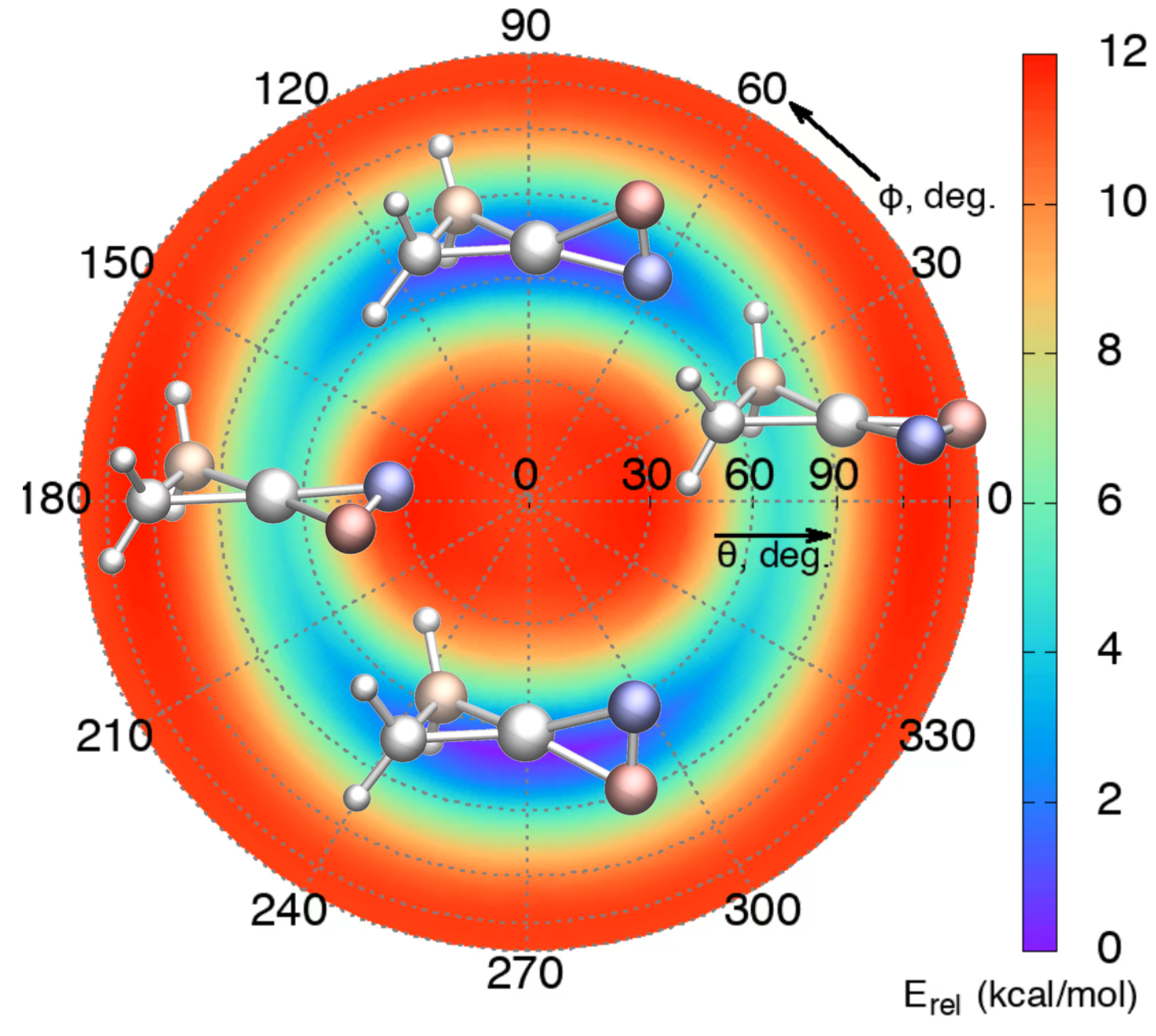
Racemization between two tetrahedral forms via planar transition state is realized in sub-picosecond time scale.
Zeolite Catalysis by QM/MM Modelling
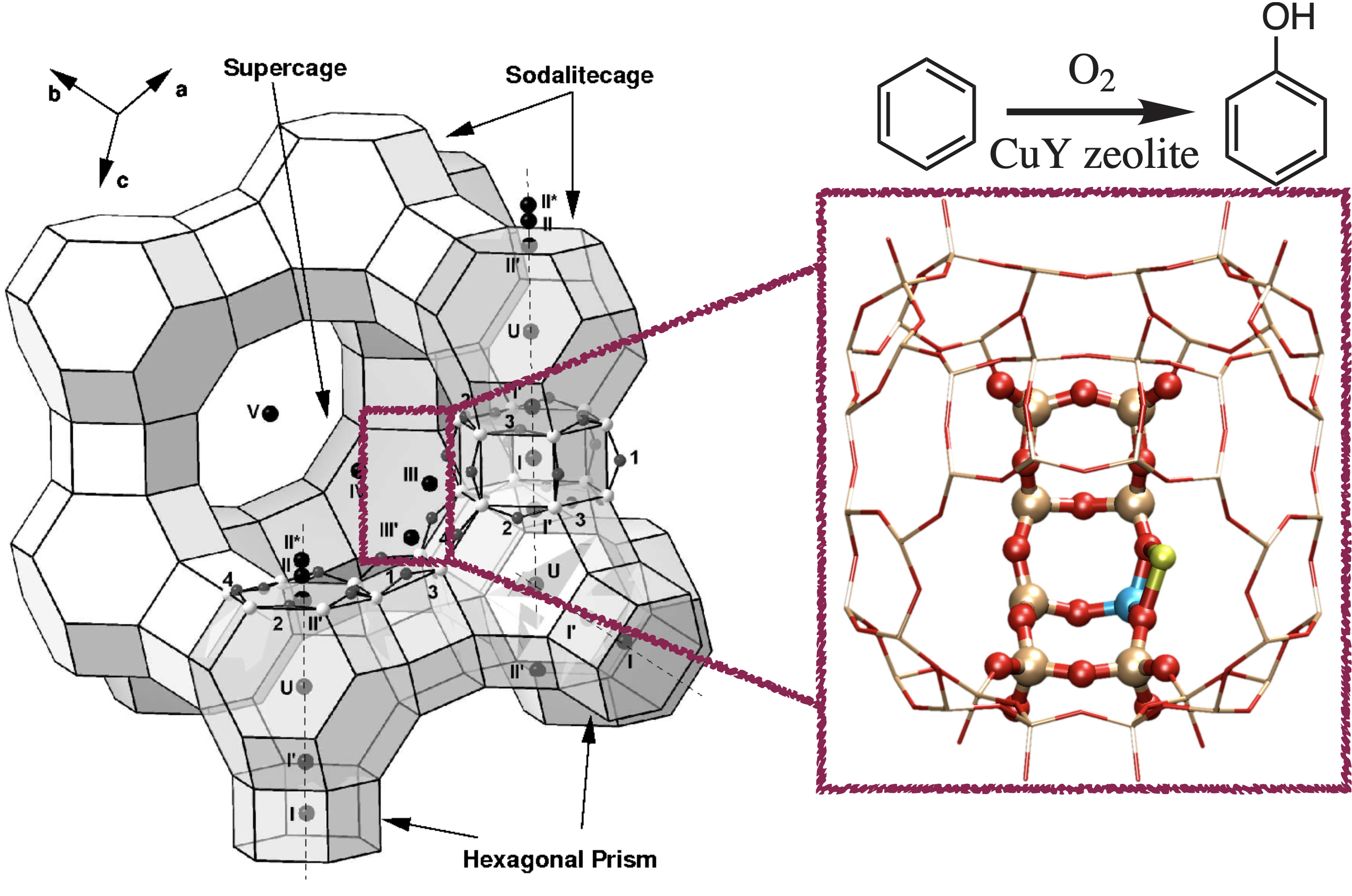
Adsorptions of dioxygen and benzene to Cu-zeolite are studied through structural, energetical, and spectroscopic analyses, and elementary steps of catalytic conversion of benzene to phenol using dioxygen are proposed.
Watson-Crick (WC)-like Tautomerization Pathways in RNA by QM/MM Modelling
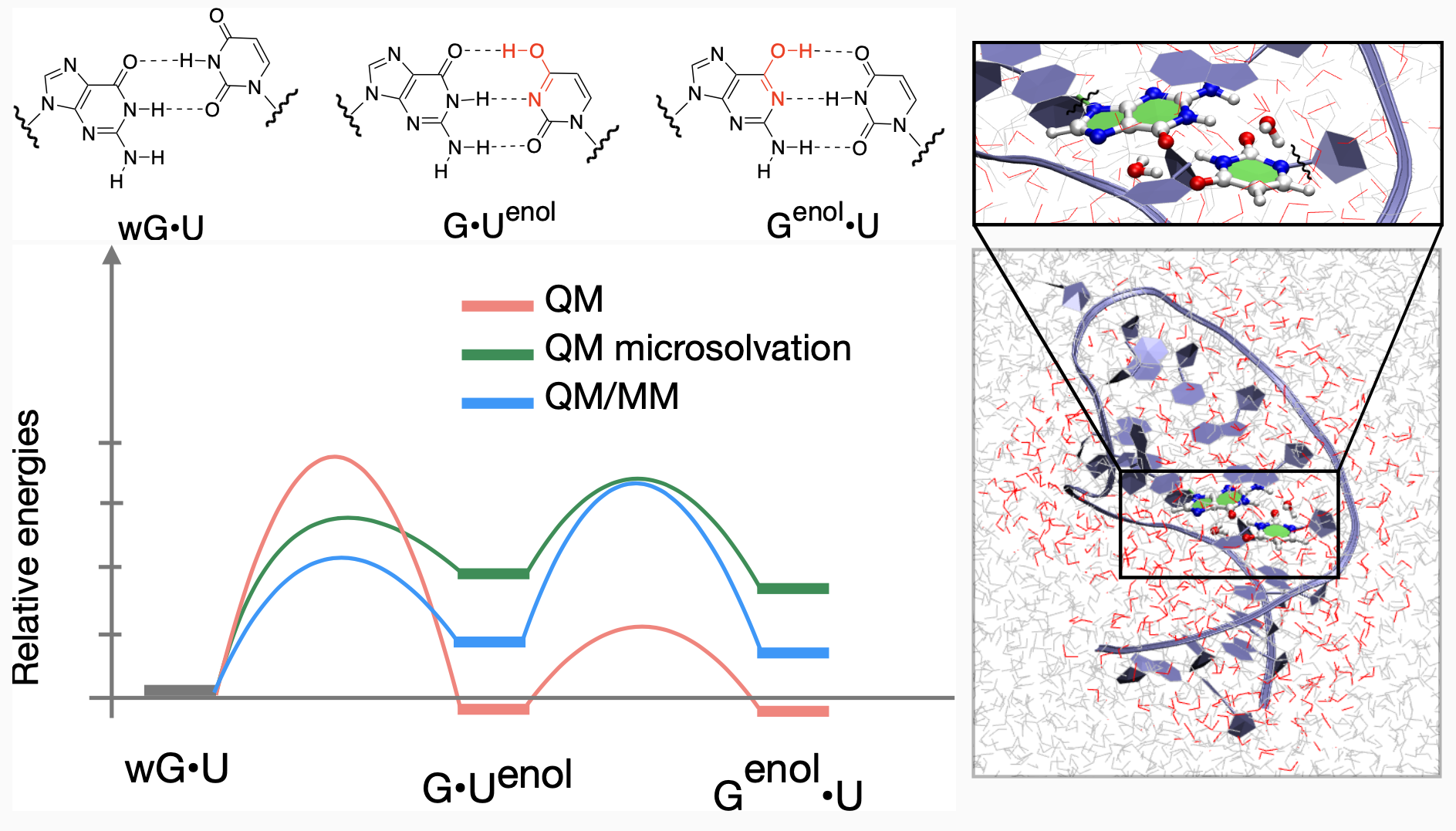
Reaction pathways of guanine-uracil enolic tautomerization from wobble geometry are investigated using various theoretical methods: quantum mechanics (QM), molecular dynamics (MD), and combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM).
Biophysical Interactions
Protein Chemistry: Interfacial Water Determining the Structure and Dynamics of Insulin Dimer
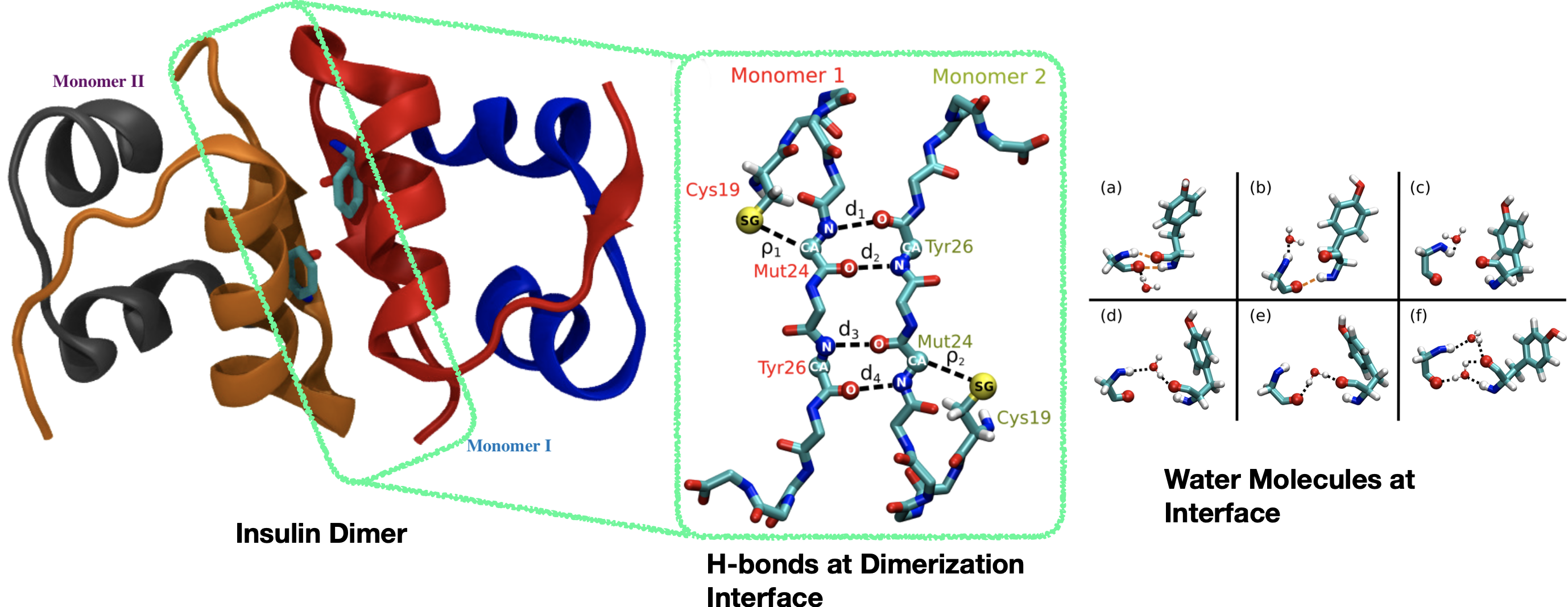
Water mediation at the dimerization interface of the insulin protein plays an ubiquitous feature, reducing direct protein-protein hydrogen bond contacts.
Protein Chemistry: Desolvation of Peptide Bond by O to S Substitution Impacts Protein Stability
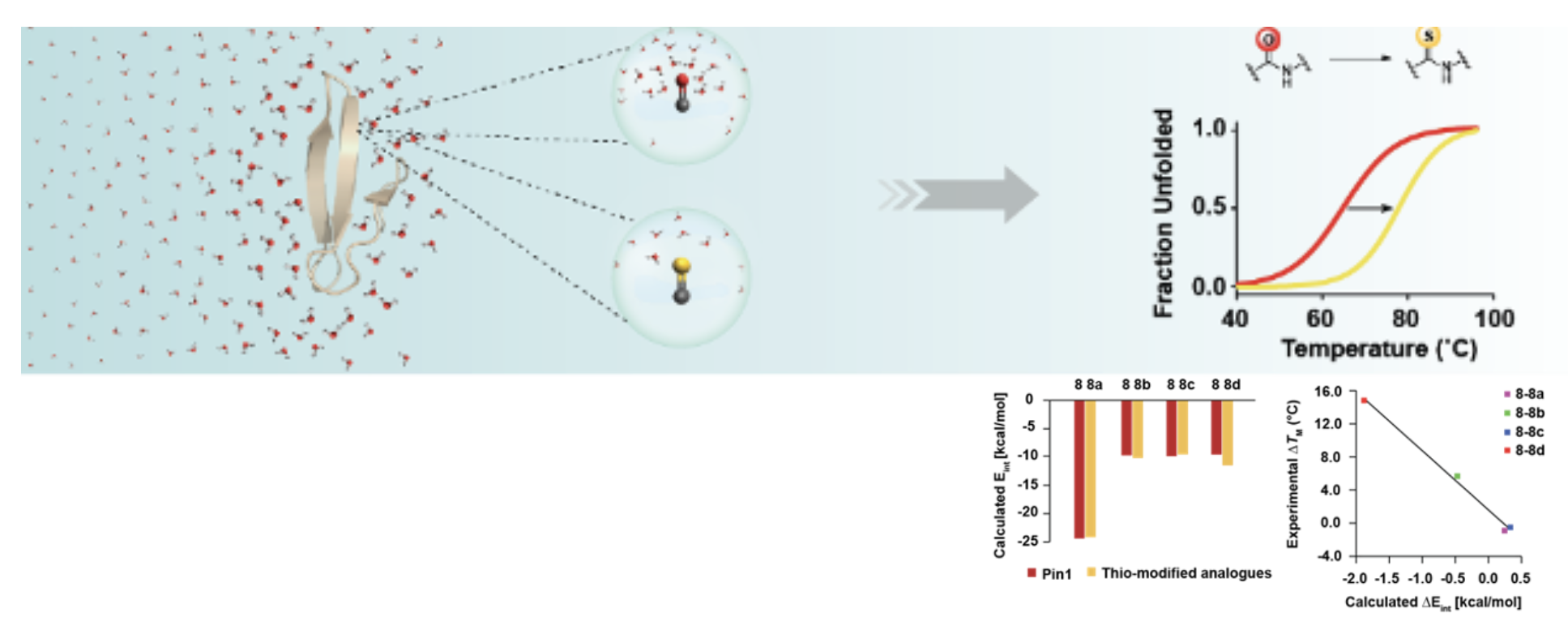
Chemical alteration (O to S) of amide bonds in proteins (peptides) reduces the microenvironment polarity leading to favorable vdW interaction and increased H-bond strength that might be proximal/distal to the modification site, eventually affecting the protein stability.
Protein Chemistry: Cosolvent Effects on Protein Denaturation
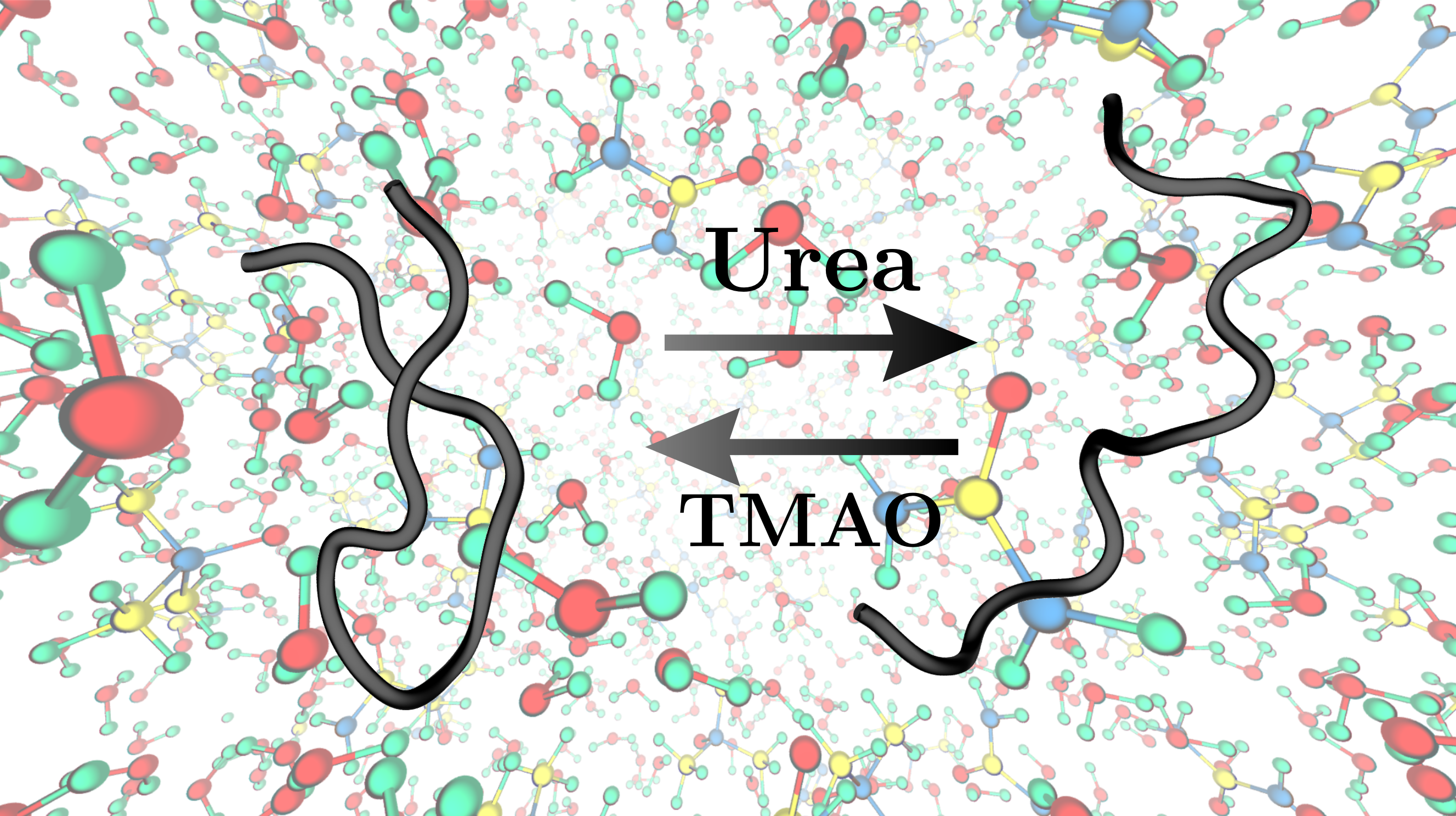
Atomistic molecular dynamics simulations are performed for proteins/side chain models in explicit solvent to characterize the nature of interactions between solvent and solute systems. Solvation free energies are computed in various solvent environments ranging from pure water to water/urea or water/TMAO (binary) to water/urea/TMAO (ternary) solutions.
Distributed Charge Model (DCM)
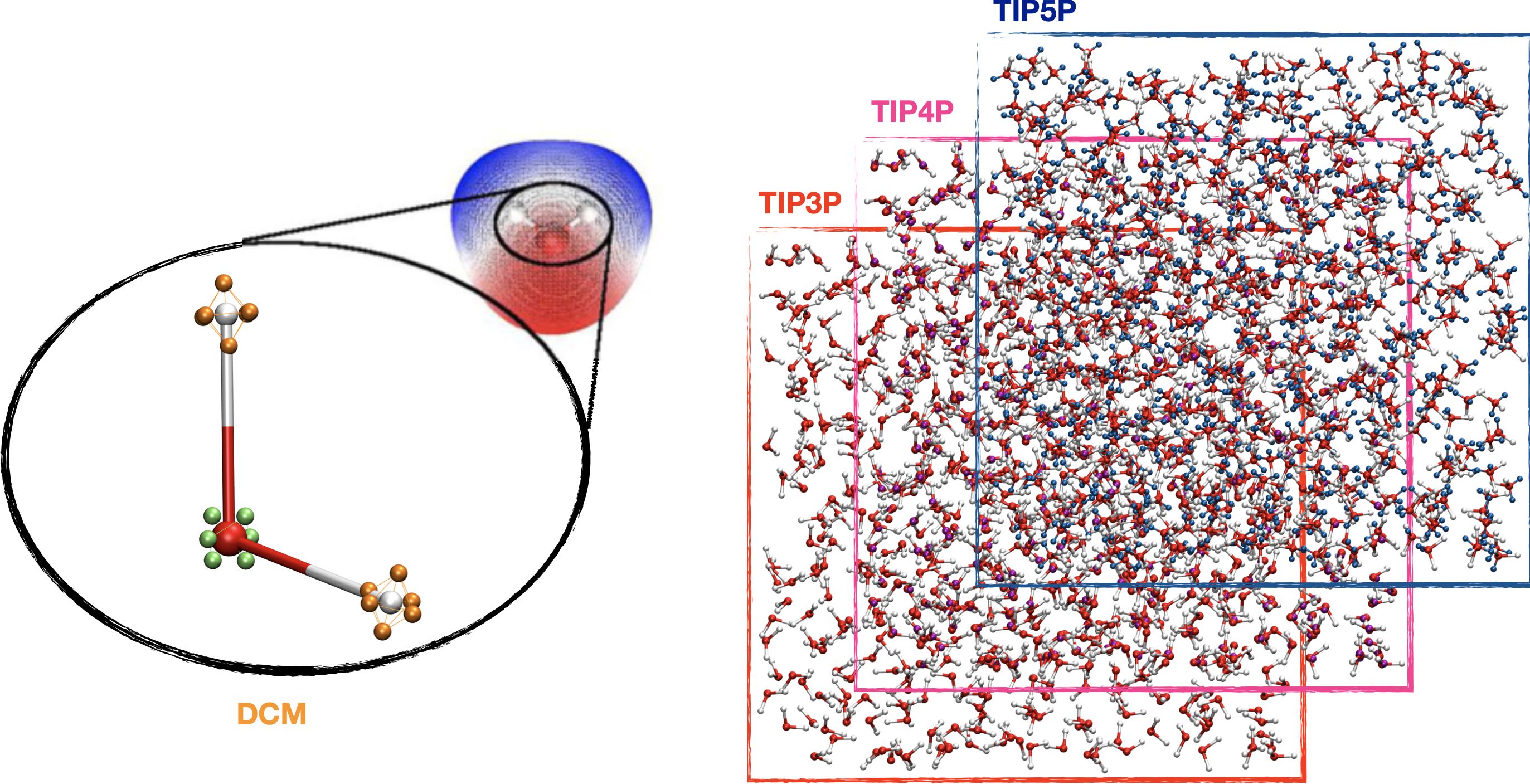
Models are developed using computational chemistry methods in order to advance our understanding on macroscopic properties of complex atomic systems in condensed-phase.